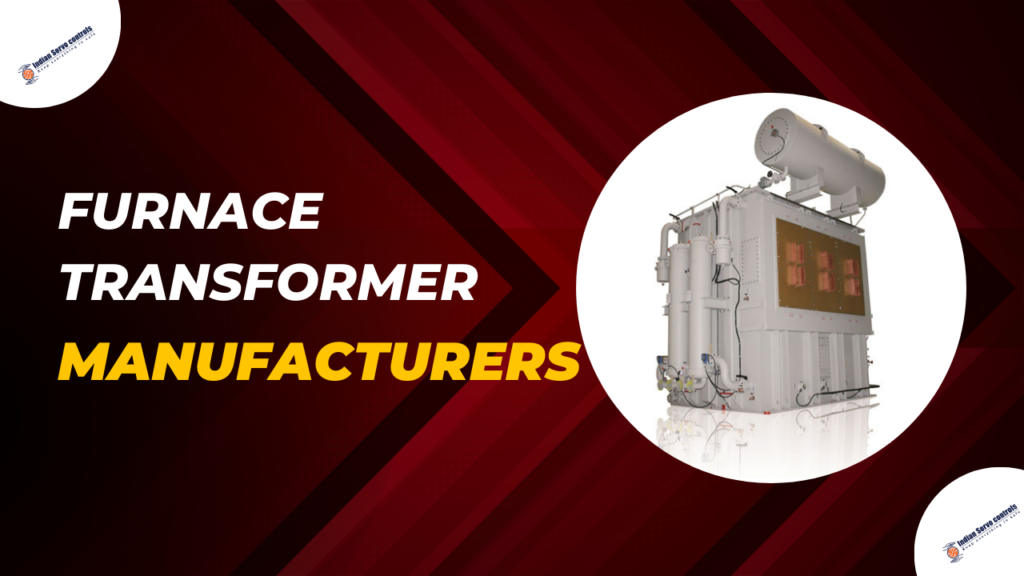
What is a furnace transformer?
Furnace Transformer Manufacturers:- A furnace transformer is a specialized electrical transformer used in industrial furnaces like electric arc furnaces and induction furnaces. It adjusts voltage levels to match the furnace’s requirements, handling high currents and harsh conditions such as extreme temperatures and electromagnetic interference. It ensures safe and efficient operation by providing the necessary electrical power in a suitable form.
Which transformer is used in furnace?
The transformer used in furnaces is called a furnace transformer. These transformers are specifically designed to handle the high currents and harsh operating conditions typical in industrial furnace environments. They may be oil-immersed or dry-type transformers, depending on the application, and they are designed to step up or step down voltage levels to match the requirements of the furnace. Furnace transformers play a crucial role in ensuring the safe and efficient operation of electric arc furnaces, induction furnaces, and other types of industrial furnaces used in processes such as metal smelting, steelmaking, heat treatment, and foundry operations.
Features of Furnace Transformer
Furnace transformers are specialized transformers used in industrial applications, particularly in steel manufacturing, where they provide power to electric arc furnaces. Here are some of the key features of furnace transformers:
- High Voltage Capacity: Furnace transformers are designed to handle high voltage levels, typically ranging from a few hundred volts to several thousand volts. This is necessary to provide the high power required for arc furnaces.
- High Current Capacity: These transformers are also capable of delivering high currents to the electric arc furnace electrodes, which are used to generate intense heat for melting metals. The current capacity can range from several hundred amps to several thousand amps.
- High Efficiency: Efficiency is crucial in industrial applications to minimize energy losses and reduce operating costs. Furnace transformers are designed with high-efficiency materials and construction techniques to maximize energy efficiency.
- Robust Construction: Given the demanding operating conditions in steelmaking facilities, furnace transformers are built to withstand high temperatures, mechanical stresses, and other harsh environmental factors. They typically feature robust insulation systems, durable enclosures, and heavy-duty components.
- Cooling Systems: To dissipate heat generated during operation, furnace transformers often incorporate advanced cooling systems such as oil circulation or forced air cooling. Effective cooling helps maintain optimal operating temperatures and extends the transformer’s lifespan.
- Protection Systems: Furnace transformers are equipped with comprehensive protection systems to safeguard against overloads, short circuits, and other electrical faults. These systems may include relays, fuses, circuit breakers, and temperature sensors.
- Control and Monitoring Features: Modern furnace transformers may include advanced control and monitoring features for remote operation, diagnostics, and preventive maintenance. This allows operators to optimize performance, detect potential issues early, and minimize downtime.
- Customization Options: Depending on the specific requirements of the application, furnace transformers can be customized in terms of voltage, current rating, size, and other parameters. This ensures compatibility with the electric arc furnace and the overall power distribution system.
Overall, furnace transformers play a crucial role in supplying reliable and efficient power to electric arc furnaces, enabling the production of molten metal for various industrial purposes.
What is the difference between the power transformer and furnace transformer?
Power transformers and furnace transformers serve different purposes and operate under different conditions, leading to several key differences between the two:
-
Application:
- Power Transformers: These transformers are used primarily for transmitting and distributing electrical power over long distances, stepping up or down voltage levels as needed for efficient power transmission.
- Furnace Transformers: Furnace transformers are specifically designed to supply power to electric arc furnaces used in industrial applications, such as steelmaking, where extremely high currents and voltages are required to melt metals.
-
Voltage and Current Ratings:
- Power Transformers: Power transformers typically handle moderate to high voltages (e.g., distribution voltages up to 500 kV) and lower currents compared to furnace transformers.
- Furnace Transformers: Furnace transformers are designed to handle extremely high currents and voltages, often ranging from a few hundred volts to several thousand volts, and currents ranging from several hundred amps to several thousand amps.
-
Operating Conditions:
- Power Transformers: Power transformers operate under relatively stable and continuous conditions, with minimal fluctuations in load and voltage.
- Furnace Transformers: Furnace transformers operate under highly dynamic and demanding conditions, experiencing rapid changes in load and voltage due to the intermittent operation of electric arc furnaces. They are subjected to high thermal and mechanical stresses during the melting process.
-
Construction and Design:
- Power Transformers: Power transformers are constructed to provide efficient and reliable power transmission, with emphasis on minimizing losses and maximizing efficiency over extended periods of operation.
- Furnace Transformers: Furnace transformers are built with robust construction to withstand the harsh operating environment of steel mills. They incorporate features such as enhanced cooling systems, heavy-duty insulation, and reinforced structural components to handle the high currents and voltages associated with electric arc furnace operation.
-
Cooling Systems:
- Power Transformers: Power transformers typically use oil or forced-air cooling systems to dissipate heat generated during operation.
- Furnace Transformers: Furnace transformers often employ advanced cooling systems, such as oil circulation or water-cooled designs, to handle the extreme heat generated during intermittent operation and maintain optimal temperatures.
In summary, while both power transformers and furnace transformers are vital components of electrical power systems, they serve distinct purposes and are designed to meet the specific requirements of their respective applications, leading to differences in voltage and current ratings, operating conditions, construction, and cooling systems.
How much does a furnace transformer cost?
The cost of a furnace transformer can vary significantly depending on several factors, including its voltage and current ratings, power capacity, construction materials, cooling system, customization options, and the supplier or manufacturer.
Generally, furnace transformers tend to be more expensive than standard power transformers due to their specialized design, high voltage and current requirements, and robust construction to withstand the demanding operating conditions in industrial settings.
To provide a rough estimate, furnace transformers for medium-sized electric arc furnaces may range from tens of thousands to several hundred thousand dollars. However, larger transformers with higher power capacities or custom designs can cost several million dollars.
It’s essential to consult with transformer manufacturers or suppliers to get accurate pricing based on your specific requirements and application needs. Additionally, factors such as delivery time, warranty, installation, and maintenance costs should also be considered when evaluating the overall cost of a furnace transformer.
Which company is best for furnace transformer?
Determining the “best” company for furnace transformers can depend on various factors, including your specific requirements, budget, location, and preferences. However, several reputable companies are known for manufacturing high-quality furnace transformers. Here are a few notable ones:
- Siemens AG: Siemens is a global conglomerate known for its expertise in various industrial equipment, including transformers. They offer a range of furnace transformers tailored to meet the specific needs of steel mills and other industrial applications.
- ABB Group: ABB is another major player in the field of electrical equipment and power systems. They provide advanced furnace transformers designed for reliability, efficiency, and durability in demanding industrial environments.
- TOSHIBA Corporation: Toshiba is known for its innovative solutions in electrical equipment, including transformers. They offer furnace transformers with advanced features and customization options to meet the requirements of different applications.
- CG Power and Industrial Solutions Limited (formerly known as Crompton Greaves): CG Power is a leading manufacturer of transformers and other electrical equipment. They provide furnace transformers with a focus on efficiency, reliability, and performance.
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation: Mitsubishi Electric is renowned for its high-quality electrical products and solutions. They offer furnace transformers designed for efficient and reliable operation in steelmaking and other industrial processes.
- Hyundai Electric & Energy Systems Co., Ltd.: Hyundai Electric manufactures a wide range of transformers, including furnace transformers, known for their robust construction and high performance in industrial applications.
- TBEA Co., Ltd.: TBEA is a prominent Chinese manufacturer of electrical equipment, including furnace transformers. They offer a comprehensive range of transformers for various industrial sectors.
When choosing a company for furnace transformers, it’s essential to consider factors such as product quality, reliability, technical support, after-sales service, and cost-effectiveness. It’s also advisable to request quotes and specifications from multiple suppliers to compare and make an informed decision based on your specific requirements.
What is a furnace transformer used for?
A furnace transformer is specifically designed to supply power to electric arc furnaces used in industrial applications, particularly in steelmaking and metal smelting processes. These transformers serve a crucial role in providing the high currents and voltages necessary to operate electric arc furnaces efficiently.
Here are the primary purposes and functions of furnace transformers:
- Power Supply: Furnace transformers supply electrical power to electric arc furnaces, which are used to melt metals such as steel, iron, copper, and aluminum. These furnaces require large amounts of electrical energy to generate the intense heat needed for metal melting.
- Voltage Transformation: Furnace transformers step up or step down the voltage from the primary power source to match the requirements of the electric arc furnace. They typically operate at high voltages to deliver power efficiently over the long distances often found in industrial facilities.
- Current Regulation: Furnace transformers regulate the current supplied to the electric arc furnace electrodes. The high currents produced by these transformers create an electric arc between the electrodes and the metal charge, generating the heat necessary for melting.
- Stability and Reliability: Furnace transformers ensure stable and reliable power supply to the electric arc furnace, even under fluctuating loads and harsh operating conditions. They are designed to withstand the high thermal and mechanical stresses associated with the intermittent operation of the furnace.
- Safety and Protection: Furnace transformers incorporate safety features and protection systems to safeguard against overloads, short circuits, and other electrical faults. These systems help prevent equipment damage, ensure worker safety, and maintain the integrity of the production process.
Overall, furnace transformers play a critical role in the steelmaking and metal smelting industries by providing the high-power electrical supply necessary for the operation of electric arc furnaces. They enable the efficient melting of metals, which is essential for the production of various industrial products.
How many volts is a furnace?
The voltage of a furnace can vary depending on several factors, including the specific type of furnace and its intended application. However, electric arc furnaces, which are commonly used in steelmaking and metal smelting processes, typically operate at high voltages to generate the intense heat required for melting metals.
In industrial settings, electric arc furnaces often require voltages ranging from a few hundred volts to several thousand volts. The exact voltage used depends on factors such as the size of the furnace, the type of electrodes used, and the properties of the metal being melted.
For example, smaller electric arc furnaces used in foundries or small-scale metalworking operations may operate at voltages in the range of 200 to 500 volts. Larger industrial electric arc furnaces used in steel mills and metal production facilities may operate at voltages exceeding 10,000 volts.
It’s important to note that the voltage of a furnace is typically provided by a specialized transformer, known as a furnace transformer, which steps up or steps down the voltage from the primary power source to match the requirements of the furnace. These transformers are designed to handle high voltages and currents associated with furnace operation.
FAQ’s: Furnace Transformer…
Q1. What is a furnace transformer?
Ans. A furnace transformer is a type of power transformer specifically designed for supplying power to electric arc furnaces used in steelmaking and other industrial processes.
Q2. What is the difference between a furnace transformer and a distribution transformer?
Ans. Furnace transformers are designed to handle high currents and voltages required by electric arc furnaces, while distribution transformers are used for stepping down voltage levels in electrical distribution systems for homes, businesses, and industries.
Q3. What are the key components of a furnace transformer?
Ans. The key components of a furnace transformer include the primary and secondary windings, core, tap changer (if applicable), insulation materials, cooling system (oil or dry-type), bushings, and monitoring/control devices.
Q4. What are the primary applications of furnace transformers?
Ans. Furnace transformers are primarily used in electric arc furnaces (EAFs) in the steel industry for melting scrap metal and producing molten steel. They are also used in other industrial applications requiring high-power electrical supplies.
Q5. How do you size a furnace transformer?
Ans. Sizing a furnace transformer involves considering factors such as the power demand of the electric arc furnace, voltage and current ratings, power factor, duty cycle, harmonic content, and safety margins based on operating conditions.
Q6. What are the cooling methods used in furnace transformers?
Ans. Furnace transformers can be cooled using oil-immersed cooling systems or dry-type (air-cooled) systems, depending on the application and design requirements. Forced-air or forced-water cooling may also be used for enhanced heat dissipation.
Q7. What are the common maintenance practices for furnace transformers?
Ans. Common maintenance practices for furnace transformers include regular inspections, oil analysis (for oil-filled transformers), checking connections, cleaning cooling systems, monitoring temperature and vibration, and timely repairs or replacements of worn components.
Q8. What are the safety considerations when dealing with furnace transformers?
Ans. Safety considerations include proper grounding, clear labeling of high-voltage equipment, protective enclosures or barriers, adherence to safety standards and regulations (e.g., ANSI/IEEE), training of personnel, and implementing emergency shutdown procedures.
Q9. What are the typical lifespan and reliability of furnace transformers?
Ans. The lifespan and reliability of furnace transformers depend on factors such as operating conditions, maintenance practices, quality of construction, and environmental factors. Well-maintained transformers can have a lifespan of several decades.
Q10. What are the advantages of using dry-type furnace transformers?
Ans. Dry-type furnace transformers offer advantages such as reduced fire hazard (compared to oil-filled transformers), lower maintenance requirements, environmental friendliness (no oil spills), suitability for indoor installations, and compliance with safety standards in industrial environments.
Keywords:-
- Furnace transformer
- Electric arc furnace (EAF)
- Industrial transformer
- Power supply for furnace
- High-power transformer
- Steelmaking transformer
- Oil-immersed transformer
- Dry-type transformer
- Cooling system for transformers
- Maintenance of furnace transformers
- Automatic voltage stabilizer
- Stabilizers
- Single phase voltage stabilizer
- Three phase voltage stabilizer
- Oil cooled voltage stabilizer
- Voltage controllers
- Three phase servo controlled voltage stabilizer
- Oil cooled servo stabilizer
- Air cooled servo stabilizer
- Three phase air cooled servo stabilizer
- Furnace Transformer Manufacturers
- Voltage stabilizers
Related Posts


6 thoughts on “Best Furnace Transformer Manufacturers, Suppliers In Delhi NCR”
Comments are closed.